Conditional statements in python
In Python, a conditional statement allows you to check if a certain condition is true, and then execute a block of code. The basic syntax of a conditional statement is as follows:
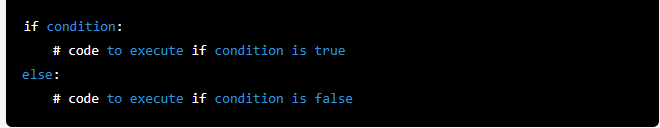
The condition is an expression that evaluates to either True or False. If the condition is true, the code within the if block will be executed, otherwise, the code within the else block will be executed.
You can also use elif (short for “else if”) to check for multiple conditions: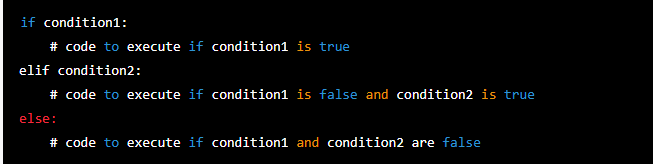
Here’s an example that uses a conditional statement to check if a variable x is greater than 0:
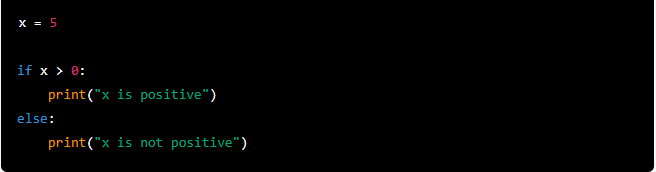
The output of the code will be “x is positive”
sparkdatabox providing python courses in Coimbatore with 100 % placement assistance
for loop in Python
In Python, a for loop is used to iterate over a sequence of items, such as a list or a string. The basic syntax of a for loop is as follows:
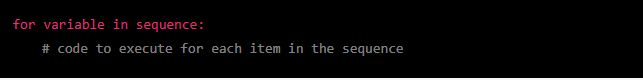
The sequence can be any iterable object, such as a list, a tuple, a string, etc. The variable is a temporary placeholder that will take on the value of each item in the sequence in turn, and the code indented under the for statement will be executed for each item.
Here’s an example that uses a for loop to iterate over a list of integers and print each one:

You can also use the range() function to generate a range of numbers to iterate over.

In this case the output will be 0 1 2 3 4
Additionally, you can use the enumerate() function to iterate over both the indices and the items of a sequence at the same time.
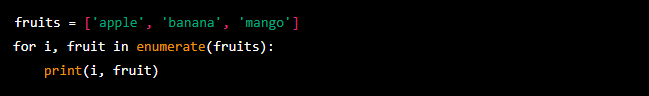
The output will be 0 apple 1 banana 2 mango
There is also a ‘while’ loop in python, which keeps executing the code inside it until the condition it tests for is no longer True.
