The term big data refers to a collection of a huge mass of data. Big data paves a way to examine, and systematically derive data, deal with the collection of data that are extremely broad and complicated to be handled by conventional data processing software or tool.
Big Data Hadoop Training in Coimbatore provides iBig Data Hadoop Training that is one of the most demanding and innovative technology fields in India. Its future is as bright as today’s with the advent of technologies like Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence, Internet of Things and Cloud Computing. A number of the world’s largest companies and IT companies are now in a race to understand big data & extract value from it. These companies are planning to invest billions of dollars to develop software solutions that would help in analyzing and extracting valuable information from these Big Data. Such solutions would help in increasing their profits and revenues.

The Big Data is of three forms, namely:
- Structured
- Unstructured data
- Semi-structured
Big data can be drilled for data and utilized in machine learning applications and other high-level analytics applications.
Structured
The data that can be collected, accessed, and handled in the mode of stable-format is named as a ‘structured’ data. Over the past few years, computer skills have reached eminent progress in advancing techniques to work with the structured data and also achieving the output from it. Still, nowadays, we are predicting concerns when the quantity of such data expands to a vast range; standard capacities are living in the mode of multiplied zettabytes. A simple example of structured data is an employee database table.
Unstructured
The data with an anonymous form is termed as unstructured data. In spite of having a massive volume of data, it also has difficulties in processing the data and achieving the output.
A simple example of unstructured data is heterogeneous data, comprising a mixture of text files, images, and videos. Organizations are loaded with a bunch of data, but sadly they are not well equipped to achieve the output from it. This is because the data is available in an unstructured format.
Semi-structured
Semi-structured data is not raw data neither typed data in a traditional database structure. It is a structured data, though it is not arranged in a logical pattern, similar to a table or graph. A collection of data obtained on the Web can be defined as semi-structured. Data assimilation primarily addresses and utilizes the semi-structured data. A perfect example of semi-structured data is private data deposited in an XML file.
Features of Big Data
The term 3Vs usually define big data:
The different features of Big data and the definitions are as follows:
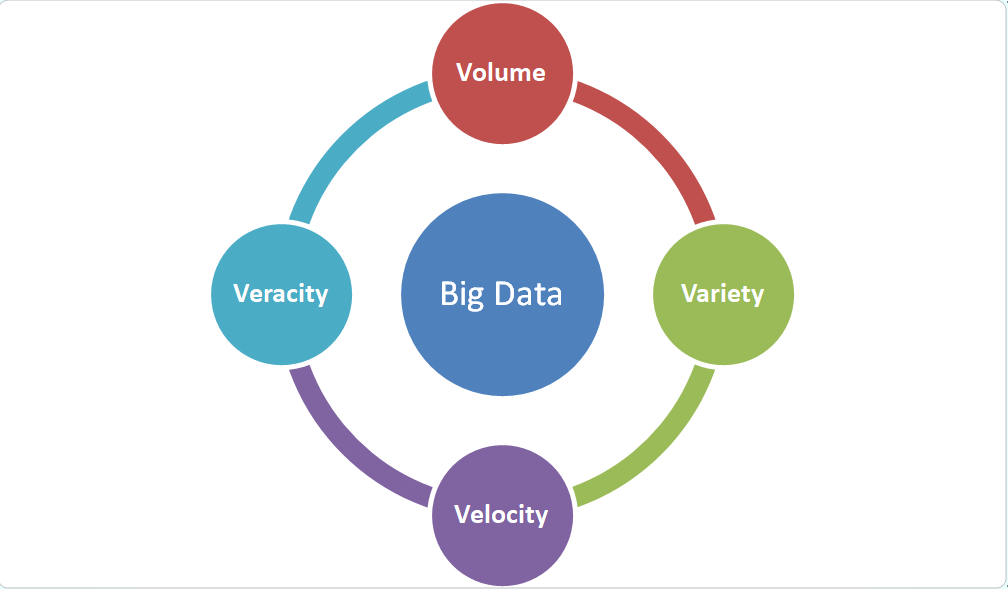
Volume
The quantity of data created and stored. The size of the data defines the latent insight, and whether it is deemed as big data or not.
Variety
The character and sort of the data. This aids in analyzing the use of data and the resulting insight efficiently. Big data extracts text, audio, video, images, and it also achieves lost parts caused by data fusion.
Velocity
The rate at which the data created and handled to satisfy the needs and hurdles that takes place through the development process. Big data is typically a real-time availability tool and are generated more frequently than small data. There are two types of velocity associated with big data such as the frequency of data creation and the frequency of processing, documenting, and resulting in the output.
Veracity
It is an extensive explanation of big data that points to the value and quality of data. The quality of data obtained can differ considerably, pretending the actual report. Data should be processed with the latest tools to share essential data.
Importance of big data
Big data can present businesses with helpful insights to their clients that can be applied to improve marketing operations and strategies to enhance customer commitment and exchange prices. Companies and brands that use big data have a rival benefit over the one who neglects the data considering they possess the knowledge to deliver more active and more skilled marketing resolutions.
Moreover, using big data empowers businesses to move towards a customer-centric approach. Prior and real-time data are used to evaluate and develop the customers’ support, thus providing companies to modernize and advance their marketing tactics and be more receptive to consumer wishes and demands.
Sparkdatabox is one of the best online software training course with free certification in coimbatore They offer Oracle Database, Java, Apache Tomcat, SQL and other courses.
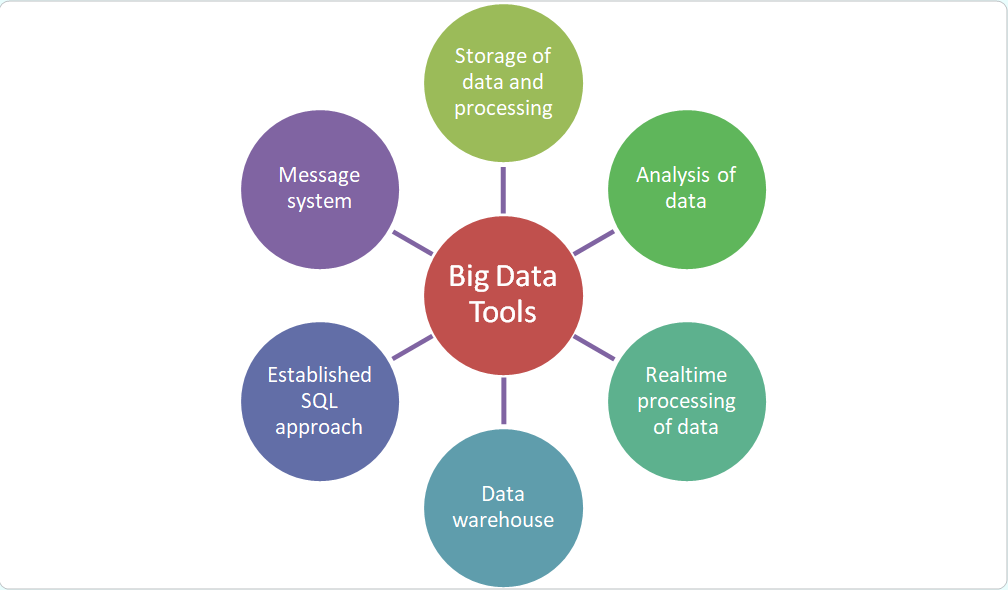
Tools of Big Data
The Working of Big Data
Big data provides you brand-new aspects that initiate increased opportunities and custom designs. Big data possess three important activities:
1. Integration
Big data draws the data together from multiple different applications. Conventional data integration tools Extract, Transform, and Load (ETL) do not able to support the task. It demands advanced strategies to examine big data, which are of huge collections like terabytes and petabytes. In the process of integration, the data are brought together and processed. Ensure whether it is put into a particular format that the business critics can have a good start.
2. Management
Big data demands vast storage. The storage resolution you can achieve in the cloud, on-premises. The data can be stored in any of your desired formats. And you can make your requirements and essential processing tools to the data. You can store your data in any form you want and bring it at your required basis. The cloud is increasingly getting prevalence as it boosts the current compute specifications and empowers you to use the sources as needed.
3. Analyzing
The investment you make on big data will surely pay you back when you clearly examine and work on your data. Create data patterns with machine learning and artificial intelligence. Set the data to run.
How to store and process big data
The necessity to control big data rapidity commands specific needs on the necessary infrastructure. The computing ability expected to process large volumes and varieties of data promptly can crash a server or server cluster. Businesses should implement sufficient processing space for big data assignments to attain the necessary velocity. This can likely demand massive servers that can share the processing task and perform together in a clustered server structure.
Performing a high velocity sufficient to cost is a big hurdle. Numerous businesses are hesitant to fund in a large server to back big data workloads, especially those who do not possess 24/7 support. Therefore, public cloud computing is presently a primitive means for hosting big data operations. A public cloud provider has the capacity storage that saves petabytes of data and measures the demanded number of servers required to achieve a big data analytics task. The company just funds for the storage and estimate time worked, and the cloud cases can be set off until they required again.
To further enhance service performance, public cloud providers present big data capacities by regulated services, which involve:
- Apache Spark
- Apache Hadoop
- Google Cloud Dataproc
- Amazon Elastic MapReduce
- Microsoft’s Azure HDInsight
Whereas in cloud ecosystems, big data are stored in the following storage like:
- HDFS – Hadoop Distributed File System
- Amazon S3 – Amazon Simple Storage Service
- Relational databases
- NoSQL databases
Big data uses and applications
- Product Development & Entertainment
- Automobile
- Insurance
- Education
- Security Systems
- Drive Innovation
- Predictive Maintenance